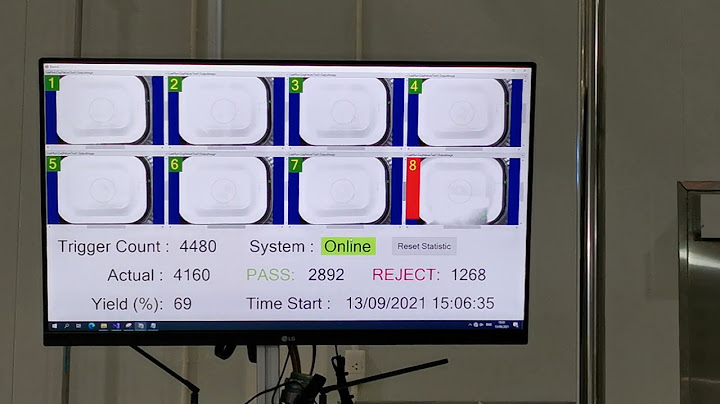
น้องๆอาจจะเคยเห็นหรือเคยได้ยินผ่านหูผ่านตามาบ้าง แต่อาจจะยังไม่รู้ว่า Isometric คืออะไร พี่ๆ Lighthouse เลยจะมาอธิบายกันแบบง่ายๆ ให้น้องๆ สามารถนำเทคนิคนี้ไปใช้ในงานของตัวเองได้🦾 📐 คำว่า “ไอโซ (ISO)” มาจากภาษากรีกซึ่งแปลว่า “เท่ากันหรือเหมือนกัน” และคำว่า “เมตริก” (Metric) หมายถึง หน่วยการวัด เมื่อนำคำทั้งสองมารวมกันเป็น ไอโซเมตริก (Isometric) จึงหมายถึง ภาพ 3 มิติ ที่มีด้านเท่ากันทุกด้านและมีขนาดเท่ากับของจริง ดังนั้นภาพไอโซเมตริกจึงเป็นภาพ 3 มิติที่เขียนง่ายเพราะมีมุมเอียง สัดส่วนที่แน่นอน ถ้าอธิบายให้ละเอียดขึ้นอีกหน่อย ภาพไอโซเมตริก คือ การเขียนภาพ ด้านหน้า ด้านข้าง และด้านบน โดยที่ขอบงานจะตั้งตรงขึ้นในแนวดิ่ง ชิ้นงานจะถูกสมมติให้วางเอียงไปด้านหน้าประมาณ 35 องศา 16 ลิปดา ซึ่งจะได้ภาพด้านข้างเอียงทำมุม 30 องศากับแนวระดับเท่ากันทั้งสองด้าน หรือถ้าจะพูดง่ายๆ Isometric Drawing คือ การเขียนรูปสามมิติที่มีขนาดเท่าขนาดงานจริง โดยด้าน 2 ด้าน ทำมุม 30 องศากับแกนตั้งนั่นเอง 🏗 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF CLOSING LOOPS FOR CANINE RETRACTION. �����Ե ��Թ��� ����ҡó� Varintra Ungbhakorn �����Ҩ�������֡�� �.��.��. 侺���� ൪����������.��. ��Է��� ����ҡó� Paiboon Techalertpaisarn, Ph.D.Prof Variddhi Ungbhakorn, Ph.D. ����ʶҺѹ ����ŧ�ó�����Է�����. �ѳ�Ե�Է����� Chulalongkorn University. Bangkok. (Thailand). Graduate School. �дѺ��ԭ�������������´�Ң��Ԫ� �Է�ҹԾ�����Һѳ�Ե. �Է����ʵ�� (�ѹ������Ѵ�ѹ) Master. Science (Orthodontics) �շ�診����֡�� 2546 ���Ѵ���(��) �ѵ�ػ��ʧ��ͧ����Ԩ�¤�� �������º��º��Ҥ����秵֧�ͧ��ʫԧ�ٻ�������ҡ��äӹdz�����ɮպ��ͧ��ʵԡ�������Шҡ��÷��ͧ �����������ҧ����ʫԧ�ٻ���Ѵ�ҡ�Ǵ���硡������ʹ����Ҵ 0.016x0.022 ���� �ӹǹ 4 �ٻẺ�ٻẺ�� 5 �ٻ ���� vertical helical loop, T-loop, Opus90 loop ��� helicalT-loop ������Ѵ��ǹ����Ѵ��ǹ���������ѵ����ǹ����������ç�����ҡ��äӹdz�ҧ��ɮ��ҡ����ش �����Ѵ��Ҵ�ç��Ǣ�ҹ�Ѻ�Ңͧ�ٻ����дѺ�����ҡ����ͤ���Ƿ��������ͤ���Ƿ 0.50, 1.00, 1.50, 2.00, 2.50 ��� 3.00 ��. ������´��ٹ���������ʵԧ����չ��� LF plus ���º��º��Ҥ����秵֧�ͧ��ʫԧ�ٻ��� 4 �ٻẺ �����ҡ��äӹdz�ҧ��ɮ���Шҡ��÷��ͧ ����ʶԵԷ��ͺ�������¢ͧ��Ъҡ����Ƿ���дѺ����Ӥѭ .05 �š���Ԩ�¾���� ��Ҥ����秵֧�ͧ vertical helical loop, T-loop, Opus90loop ��� helical T-loop �����ҡ��äӹdz�����ɮպ��ͧ��ʵԡ�������ҡѺ33.80, 23.80, 19.60 ��� 23.50 ����/��. ����ӴѺ ��ǹ��Ҥ����秵֧�����ҡ��÷��ͧ��ҡѺ 81.90, 59.63, 55.94 ��� 47.66 ����/��. ����ӴѺ ��÷��ͺ�������¢ͧ��Ъҡ����Ǿ���� ��Ҥ����秵֧�ͧ��ʫԧ�ٻ��� 4 �ٻẺ�����ҡ��÷��ͧ�����ҡѺ��Ҥ����秵֧�����ҡ��äӹdz�ҧ��ɮշ���дѺ����Ӥѭ.05 (p = .000) �ѧ��鹷�ɮպ��ͧ��ʵԡ����֧�������������й�����ӹdz�Ҥ�Ҥ����秵֧�ͧ��ʫԧ�ٻ ���ҧ�á����ŷҧ��ɮ��ѧ�ջ���ª��㹡�÷�����Һ�Է�ԾŢͧ���������¹�Ѵ��ǹ��ҧ� �ͧ�ٻ��ͤ���ѵ����ǹ����������ç��Ф�Ҥ����秵֧ ���Щй�鹷�ɮպ��ͧ��ʵԡ��������Ըա�÷ҧ��Ե��ʵ�����Ҩ����ǹ����㹡���͡Ẻ ������㨤س�ѡɳТͧ��ʫԧ�ٻ�ѹ�Դ�ҡ�Ѵ��ǹ��ҧ� �ͧ�ٻ�� ���Ѵ���(English) The objectives of this research is to compare values of the stiffnesses of theclosing loops calculated by Castigliano's theorem to those by experimental results.Selected samples are the closing loops constructed from 0.016x0.022 inch stainlesssteel wire. They are four types of closing loops, namely, vertical helical loop, T-loop,Opus90 loop and helical T-loop, each with five samples. The configuration of eachtype of loops corresponds to the configuration which gives maximum MIF ratio theoretically.The activated forces are measured by applying the force parallel to the horizontal legsof each loop using Lloyd universal testing machine LF plus. The activated displacementsare 0.50, 1.00, 1.50, 2.00, 2.50 and 3.00 mm. The resulting values of loop stiffnessesobtained from experiment are then compared to the theoretical stiffnesses by usingthe test statistic one-sample t-test at .05 significant level. The Castigliano's theorem predicts the values of loop stiffnesses of the verticalhelical loop, T-loop, Opus90 loop and helical T-loop to be 33.80, 23.80, 19.60 and23.50 gm/mm respectively. The experimental values of the corresponding closing loopsare 81.90, 59.63, 55.94 and 47.66 gm/mm respectively. From the t-test, it is found out thatthe stiffness values of the four closing loops obained from experiment are not equal tothose from theory at .05 significant level (p = .000). Hence, the Castigliano's theorem is,not suitable for calculating the loop stiffness. However, the theoretical results still showthe influence of variable dimensions of the closing loop on the MIF ratios and stiffnesses.Therefore, the Castigliano's theorem is still the mathematical method which may facilitatethe design and understand the characteristics of the closing loop formed from various dimensions. ���ҷ������¹�Է�ҹԾ��� �ӹǹ˹�Ңͧ�Է�ҹԾ��� 108 P. ISBN 974-17-3514-6 ʶҹ���Ѵ���Է�ҹԾ��� ���Ӥѭ STIFFNESS, CLOSING LOOP, CASTIGLIANO, CONFIGURATION, M, F �Է�ҹԾ���������Ǣ�ͧ |

กระทู้ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
การโฆษณา
ข่าวล่าสุด
การโฆษณา
ผู้มีอำนาจ
การโฆษณา
ถูกกฎหมาย
ช่วย

ลิขสิทธิ์ © 2024 th.ketajaman Inc.